Internet of Things in the Automotive Industry: Solutions for Vehicles, Smart, and Connected Cars

Key takeaways
- Discover more about what automotive IoT is and what the future holds for the industry.
- Get useful information on the benefits of the implementation of the internet of vehicles.
- Is there a downside of the automotive IoT? Let’s break down each disadvantage and find out how to solve it.
- Read how IoT transformed the whole concept of vehicles development and figure out what are the perspectives for the IoT industry.
- Learn about the big players in the field of autonomous vehicles and what solutions they offer for further improvement of AV.
- Find out about the most popular IoT in the automotive sector use cases like predictive maintenance, insurance, fleet management, and others.
- Developing an IoT app is an arduous task. Learn about the general points you may face while developing a solution for the smart vehicle and the Internet of Things. Also, discover how to overcome certain challenges connected with it.
- Read how we contributed to the IoT and automotive industry by enabling car drivers to charge their cars remotely with the ability to control the charger via the app while sharing the rights with the appointed users.
Advanced technologies like IoT have empowered numerous industries, including automotive, giving businesses the necessary levers to embrace automation, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. However, what is automotive IoT exactly, and what happens when these two worlds collide? The changes that IoT brought into the automotive domain are groundbreaking, but what we can say for sure is that it’s a step closer to what we see in science fiction movies. What once was a figment of imagination now is a briskly evolving phenomenon.
A distant future in which cars become intelligent companions, quickly navigating smart cities and ensuring our safety on the road is not that distant already. Thus, the IoT in the automotive market is gaining momentum at a rapid pace and brings us closer to the fantastic visions we once only saw on the screen. According to the statistics, more than 400 million smart cars are predicted to be in operation by 2025.
To avoid getting lost in this fast-growing market, we’ve created a guide to help you understand the Internet of Things concept and how it facilitates the transformation of the entire automotive industry.
What is automotive IoT?
So, what is automotive iot? It encompasses the incorporation of sensors, devices, cloud technologies, and applications within vehicles, creating a sophisticated predictive maintenance system, car connectivity, and fleet management. By leveraging embedded IoT solutions, vehicles have evolved into highly intelligent entities. The IoT enables automotive manufacturers to introduce numerous innovations, including highly-discussed self-driving cars. This comprehensive platform expands IT possibilities, providing a foundation for groundbreaking advancements in the automotive industry.
To get a real picture of IoT perspectives, imagine that you will come out of the house one day and your car is already summoned from the garage to the driveway as it knows that, according to your calendar, you have a ride for today. On your way, a car will stream some podcasts chosen according to your preferences. On arriving, it will drop you off and find a parking lot. After getting things done, you will summon your car to where you are standing only with one click on the smartphone and drive back home.
It may seem a little fantastical, but it’s closer than you might imagine. All of this will be possible thanks to the further development of the Internet of Things in the automotive industry, which is already being actively incorporated into smart vehicles. According to a study by Statista, in terms of IoT-related revenue, the automotive IoT market is expected to reach 23.6 billion US dollars in 2025.
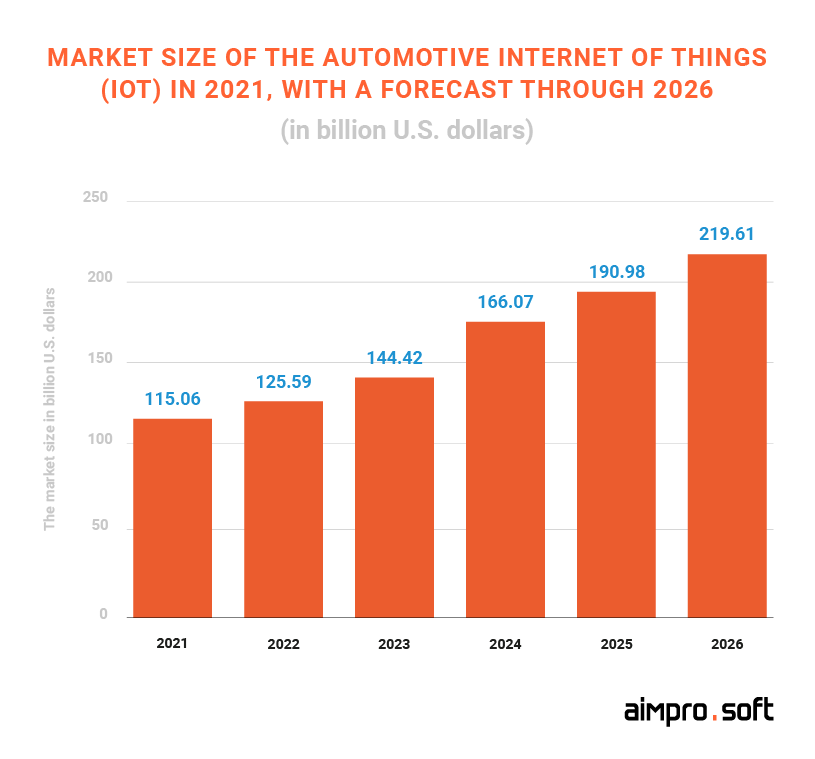
Market size of the automotive Internet of Things (IoT) in 2021, with a forecast through 2026. Source: Statista
Now let’s explore the exciting benefits of the Internet of Things for cars industry and see how they are shaping the future of mobility. From improving safety and efficiency to optimizing maintenance and delivering a personalized driving experience, the benefits of IoT in the automotive industry are truly astounding.
Benefits of IoT in the automotive industry
Integrating the Internet of vehicles has brought many benefits to car manufacturers and users alike. IoT technologies have enabled automakers to increase vehicle productivity, optimize maintenance processes, and improve safety features. Real-time data collection and analysis ensure predictive maintenance, reduction of downtime, and improvement of overall efficiency. Let’s discuss all these in more detail and find out how your business can profit from them.
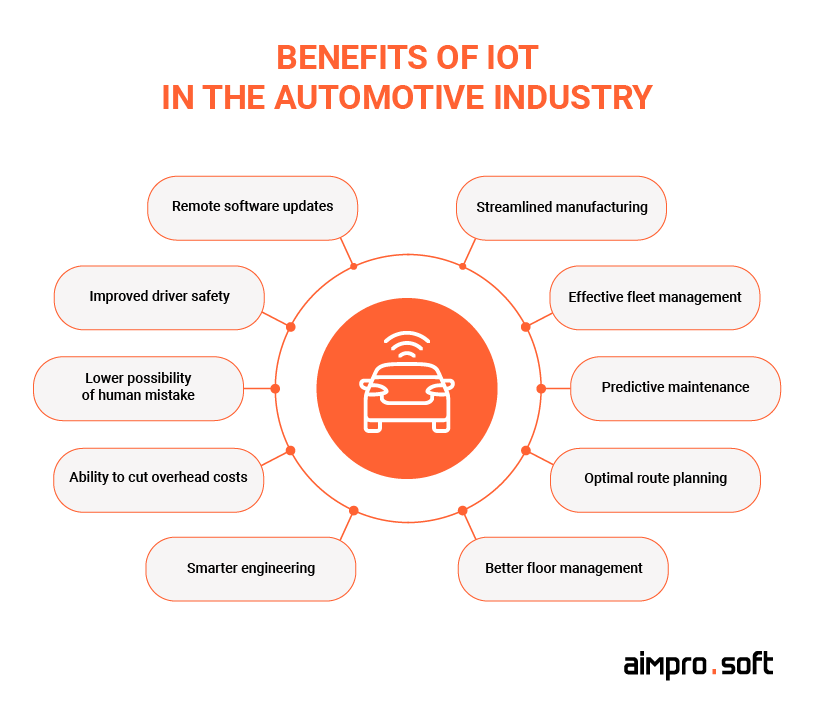
Benefits of IoT for automotive industry
Streamlined manufacturing & floor management
Car manufacturers can monitor various aspects of the production process by placing IoT devices and sensors throughout a production line in real-time. This includes monitoring machine performance, tracking inventory levels, and analyzing production data. With a clear picture of the production floor, IoT automotive companies can identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows and improve overall efficiency, ultimately leading to increased productivity and cost savings.
Effective fleet management
Integrating IoT technology into fleet management allows vehicles to be tracked and monitored in real-time, leading to efficient fleet operations. IoT sensors collect and transmit data on vehicle location, fuel consumption, driver behavior, and maintenance requirements. This information helps fleet managers optimize routes, monitor fuel efficiency, plan maintenance, and enforce safety regulations.
Predictive maintenance
Such a benefit allows manufacturers to anticipate and address maintenance needs before they lead to costly breakdowns. IoT sensors can detect anomalies, monitor component health, and predict potential failures by collecting and analyzing real-time data from vehicles and equipment. Predictive maintenance improves reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for manufacturers and users alike.
Optimal route planning
Optimal route planning based on iot for automotive allows logistics and transport companies to optimize delivery routes, reduce fuel consumption and improve operational efficiency. IoT systems can calculate the most efficient ways using live data on road conditions, weather, and vehicle performance. This results in shorter delivery times, improved customer satisfaction, and cost savings by minimizing fuel consumption and optimizing resource allocation.
Enhanced customer-oriented manufacturing
Manufacturers can gain valuable insights into customer preferences, requirements, and usage patterns using IoT devices and analytics data. This information lets them personalize products, speed up manufacturing processes, and manage just-in-time inventory. Manufacturers can deliver customized vehicles, improve the user experience and respond faster to customer needs. In the same way, customer-oriented IoT production increases clientы satisfaction, strengthens brand loyalty, and enhances competitiveness in the marketplace.
Remote software updates
The implementation of iot for automotive allows software embedded in a car to be updated remotely, eliminating the need for physical visits to service centers. With distant software updates, manufacturers can improve vehicle performance, eliminate potential vulnerabilities and introduce new features without inconveniencing car owners. This simplified process increases convenience, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures a smooth and efficient user experience.
Improved driver safety
IoT technology plays a key role in enhancing driver safety by providing advanced driver assistance systems like ADAS (Advanced driver assistance systems). ADAS technologies, enabled by IoT sensors and connectivity, offer features such as collision detection, lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking. These systems constantly monitor the vehicle’s surroundings, warn drivers of potential dangers, and in some cases, can even intervene to prevent an accident.
Reduced possibility of human mistake
The chance of human mistakes is considerably decreased by IoT integration in automotive operations. By automating processes and making data-driven decisions, IoT technologies minimize reliance on manual intervention and the associated risks. For example, autonomous cars equipped with IoT sensors, cameras, and advanced algorithms can navigate roads, detect obstacles, and make driving decisions more accurately and precisely than human drivers.
Ability to cut overhead costs
The adoption of IoT in the automotive sphere helps reduce overhead costs by streamlining processes and improving operational efficiency. A McKinsey study claims that IoT-based predictive maintenance lowers the cost of servicing factory equipment. Namely, by obtaining real-time data on inventory levels, demand patterns, and production requirements, manufacturers can optimize procurement, production, and distribution processes. In addition, predictive maintenance based on IoT enables timely service and maintenance of cars, reducing unexpected breakdowns and minimizing associated costs. Using IoT technology, automotive companies can identify cost-saving opportunities, increase productivity and improve overall profitability.
Smarter engineering
The introduction of the Internet of Things cars can help manufacturers gain useful insights into critical business aspects that can directly affect sales, such as car design and service offerings. The information gathered on how drivers interact with the automobile, which functions are used most often and which are unhelpful to the driver, enables manufacturers to change the car’s design.
The IoT car also enables communication between the end user and the manufacturer and alerts them to system faults in the car. This makes it possible to provide the driver with individualized services like real-time maintenance, technical assistance, and updates.
Challenges in IoT implementation
While adopting the internet of vehicles in the automotive sector brings many benefits, it is essential to recognize that no system is perfect, and problems can arise. However, understanding these problems and adopting effective strategies to minimize such issues will contribute to a successful IoT implementation. In this section, we’ll discuss some common challenges with IoT in the automotive industry and outline how to overcome them.
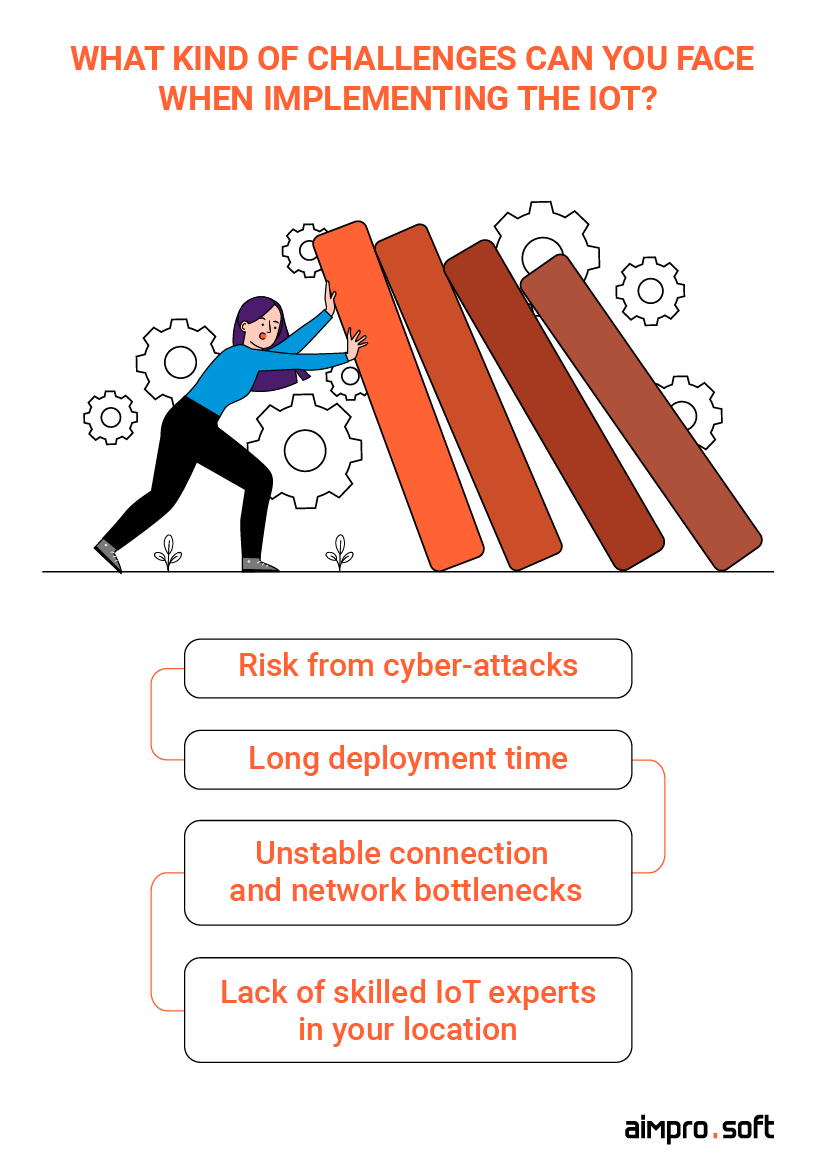
Challenges you may encounter when implementing the IoT
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is one of the main obstacles to the IoT adoption in the automobile sector. Cars and IoT systems create potential entry points for cyber-attacks and unauthorized access. Protecting the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data and securing communication networks becomes paramount.
So how to minimize this problem?
To solve this issue, robust cyber security measures, such as encryption, authentication protocols, and regular security audits, must be implemented to safeguard against potential cyber-attacks and protect users’ sensitive information.
Long deployment time
The integration of IoT in the automotive field can often lead to challenges related to long deployment times. Integrating IoT devices, sensors, and systems into existing infrastructure and vehicles can take considerable time and effort.
How can I reduce the time required for deployment?
Minimizing deployment time requires careful planning, effective project management, and close collaboration between stakeholders. Standardized and modularised IoT solutions can also help simplify deployment and speed up the implementation process.
Connection stability and network bottlenecks
Maintaining stable and secure connections between IoT cars, vehicles, and network infrastructure can be a challenge. Factors such as limited network coverage, signal interference, and congestion can affect the reliability and performance of IoT systems.
How to deal with this drawback?
Conducting a thorough network assessment and eliminating coverage limitations or signal interference can help maintain stable connections. Introducing edge computing techniques where data is processed locally can reduce network bottlenecks and minimize reliance on centralized servers, improving overall system performance.
Lack of required IoT skills
When implementing IoT project, you can face challenges related to a shortage of skilled professionals with expertise in IoT technologies. Introducing IoT requires a combination of software, networking, and data analytics skills.
How to solve this problem?
The best solution to this problem is to outsource in the absence of local talent, namely, working with IoT technology vendors. These companies often have an extensive internal pool of specialists in the field and required experience in working with IoT technologies. For example, at Aimprosoft, we have vast experience in the IoT sphere and are ready to apply it when developing software for your IoT project. For more than ten years, we have been creating IoT-powered software solutions for companies in a variety of industries, including e-learning, healthcare, e-commerce, automotive, and others.
While adopting IoT in the automotive sphere comes with various challenges, such as cybersecurity risks, long deployment times, connectivity stability issues, etc., these obstacles can be effectively overcome with the right strategies and measures. What if we told you that the integration of the industrial internet of things into the automotive industry is just getting started? Let’s assess the impact that IoT cars have already made on it and its prospects.
Impact of the Internet of Things on connected cars, smart cars, and vehicles
The first huge step of the Internet of Things for cars was the embedding of computer dashboard diagnostics in 1995 and the utilization of a 16-pin data port that accessed the vehicle’s computer network in 1996. Chrysler was the first who presented a Bluetooth-capable system in their cars in 2000. In 2006 car drivers could see the appearance of USB slots, which were designed for a better experience of In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI).
It took not that long for IoT to start prospering in the automotive area, but it has already made a huge impact on vehicles’ whole concept and functioning. People don’t see cars as simple transportation anymore. The active integration of IoT technologies has resulted in the appearance of connected and smart cars, and in the longer perspective — autonomous vehicles.
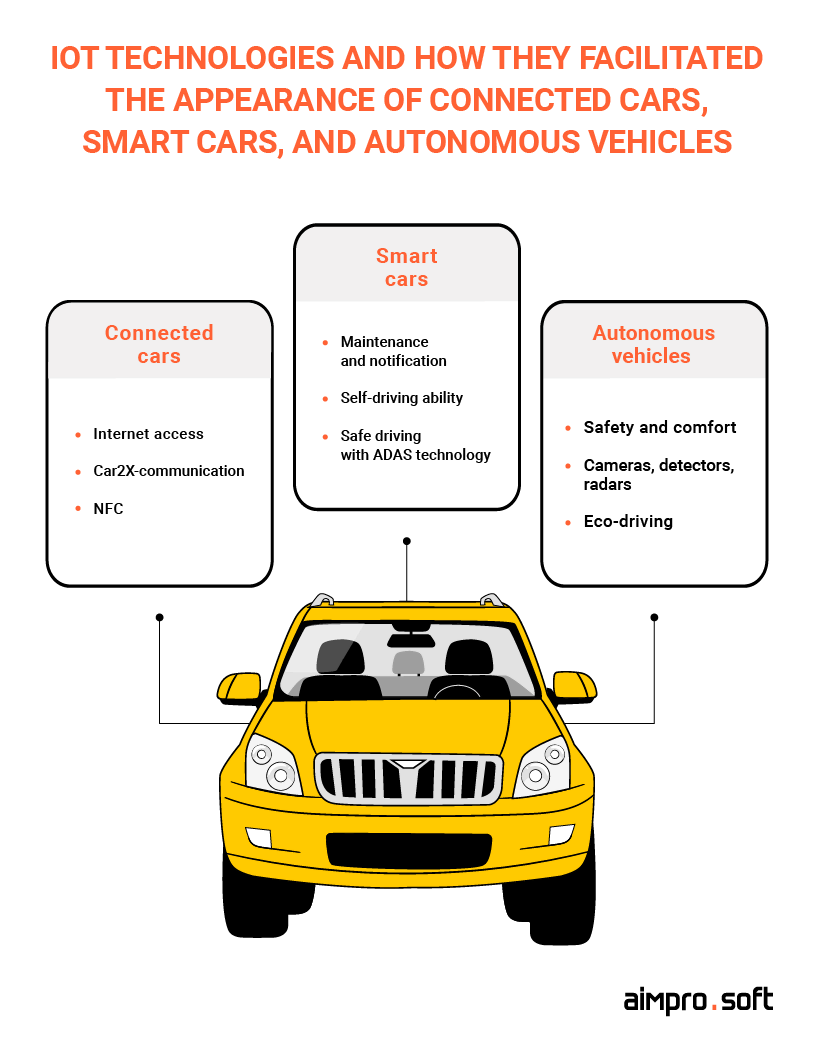
IoT technologies facilitated connected cars, smart cars, and autonomous vehicles
Connected cars
A connected car internet of things is a vehicle with internet access and connection of devices inside and outside. There are three main IoT technologies that are actively used in cars for connection:
- advanced telematics;
- Car2X-communication;
- NFC.
For instance, Bluetooth and WiFi pairing has gotten quicker and simpler thanks to short-range wireless technology like Near-field communication (NFC). Besides this, NFC also has a significant role in developing smartphone-centric solutions and new business models in the spheres of fleet management, car rental, and sharing.
Сars and the Internet of Things enable data exchange, which is carried at the following five levels:
- vehicle to infrastructure (V2I);
- vehicle to vehicle (V2V);
- vehicle to pedestrians (V2P);
- vehicle to cloud (V2C);
- vehicle to everything (V2X).
V2X combines all the levels stated above. These connections make a significant impact on the whole advancement of the road infrastructure.
- Firstly, they boost further development of connected car internet of things as data can be thoroughly collected and analyzed for a better understanding of what drivers want to see in their cars, which technologies are needed for the implementation of better city road infrastructure, and in general — determine which direction the IoT is moving towards.
- Thanks to the capabilities of the Internet of Things for vehicles, cars on the road can easily exchange necessary data for providing safety and comfort for all road users. For drivers, it is a way to receive all the required data from surrounding cars in terms of accident prevention. For the city’s street services, it is the opportunity to monitor road conditions and make all the repairs in time. The recently implemented V2P connections help pedestrians feel safer while walking on the roads (watch traffic and switch lights).
- You can get over-the-air (OTA) upgrades from the car’s manufacturer at any time or acquire other software for a more convenient in-car experience while driving a car in IoT.Such apps allow you to have real-time monitoring of a car’s condition, place all the maintenance data automatically, and thus see the overall state of affairs due to the built-in data analysis algorithms. With this data, you can make your spending wiser, more viable, and more efficient.
Smart cars
A smart car, which combines system-driven forms of AI with built-in modern electronics, is a prime example of how the automotive industry and the Internet of Things may work together.
- The smart car utilizes IoT devices that fulfill both maintenance and iot device notification functions.
- One of the stand-out characteristics of the smart car is the possibility of self-driving. With the broader spread of faster cellular 5G connection, there will be a wider field for creating new automotive IoT solutions and boosting the usage of the Internet of Things for smart cars.
- Safety is one of the most important matters of concern for all road users, and IoT in smart cars is the pathway to safer driving. The advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) were created on the basis of the IoT technologies’ implementation. With the use of IoT automotive radars and cameras, ADAS can manage vehicle and driver safety and stop possible dangers both on the road and during parking. Many cars also have teen safety tools (for example, music will not start playing until a teenager fastens his/her seatbelt or a speed limit set by a parent).
Autonomous vehicles
It’s important to say that the future of the automotive industry belongs to independent vehicles.
- Such vehicles guarantee safety on the roads and bring a new degree of the user’s comfort. The combination of analogous IoT devices like cameras, detectors, radars, inertial measurement units (IMU), etc., gives a lot of possibilities for further development of the Internet of Things for cars.
- The development of autonomous vehicles (AV) with IoT implementation will appreciatively impact the environment. For illustration, Tesla has announced their new service called Robotaxi. It’ll let every Tesla owner add via the app their auto to Robotaxi’s service and point out particular hours for sharing his/ her auto with other people. In this way, the number of automobiles and air pollution will be reduced, and it’s also a chance for car owners to defray their maintenance costs.
There is the gradation of automated driving levels, which was standardized by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). You can look through the following infographic to get more information about it.
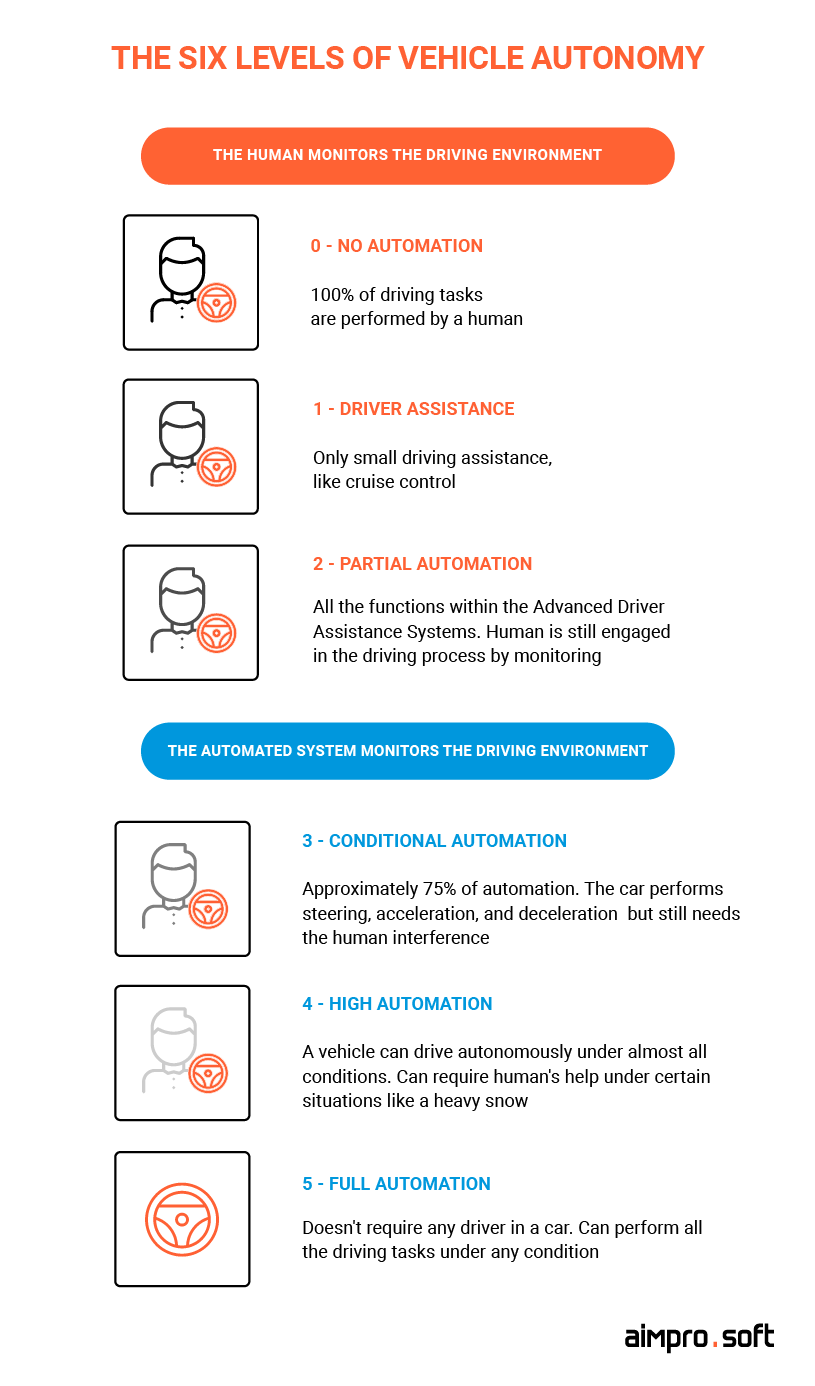
The six levels of vehicle autonomy
Currently, the big players in the field of AV are Waymo, GM Cruise, Argo AI, Tesla, ZOOX, and Chinese companies — Baidu and AutoX. Most of them intend to develop the best possible technology for autonomous driving and implement it all over in all contemporary autos. Some of them, like Argo AI, aim to deliver their technologies to other companies, similar to robotaxies or delivery businesses.
A particular process is applied to create an IoT app. Let’s look through the most popular IoT cases in the coming section.
The most common IoT use cases in the automotive industry
The possibilities for using the Internet of Things in the automotive industry are bottomless. Below, we present you with the most common cases which are actively applied now.
1. Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X)
C-V2X is an umbrella term for the IoT network that connects an auto with different road infrastructure objects. As we previously mentioned, there are different levels of data exchange. They all can be divided into “device-to-device” and “device-to-network” categories.
The first one includes:
- V2V — exchanges data about a vehicle’s place, speed, and dynamics and also helps prevent collisions;
- V2I — exchanges data between a vehicle and road infrastructure (traffic lights, lane markings, and risk booths), and enables drivers to save their time by managing traffic and overflows or ranges;
- V2P — allows a pedestrian to connect with C-V2X via the mobile app, where they can check information about city transportation or taxis.
The “device-to-network” category indicates a vehicle-to-network or vehicle-to-cloud connection. This type allows the car to be connected with cloud-based services or Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS). Such services and systems can deliver real-time data regarding weather conditions, traffic reporting, etc.
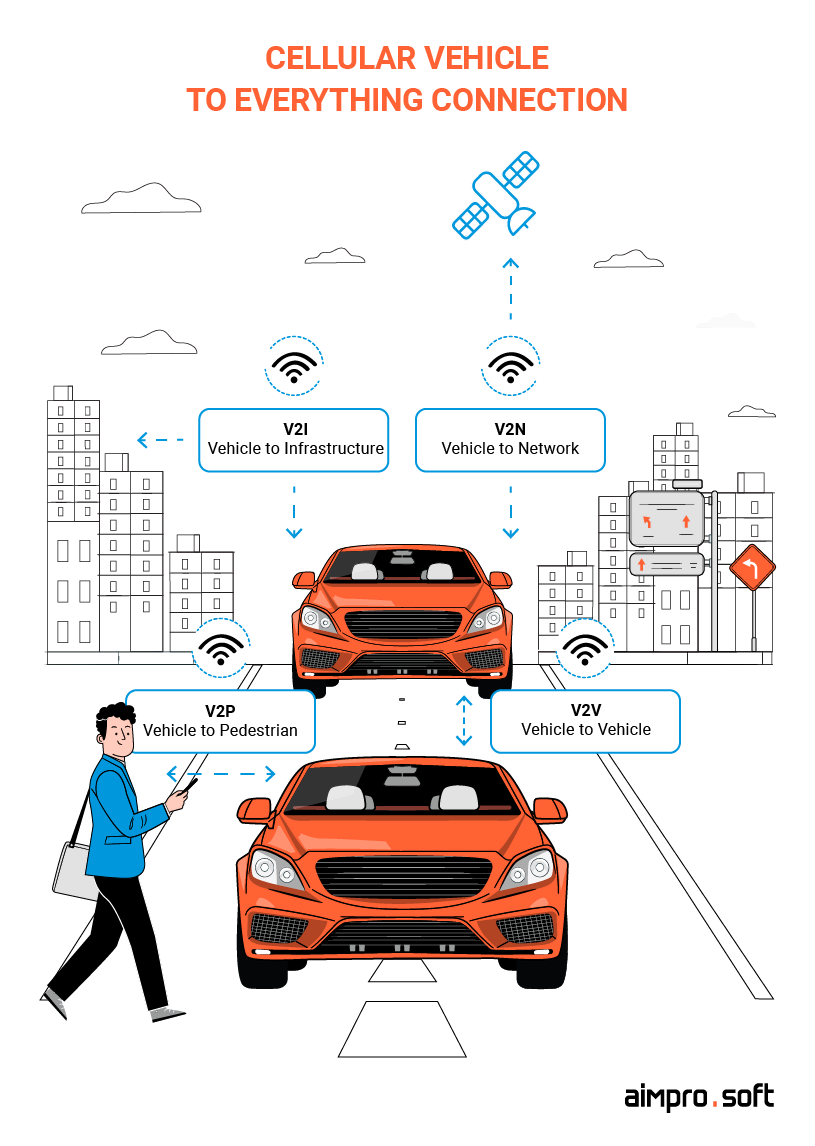
Cellular vehicle to everything connection
2. Fleet management
Thanks to IoT, fleet administration has received a new conception of workflow. IoT devices installed on vehicles collect data using RFID, GPS, and OBDII detectors. This data includes the speed, idling time, driver’s actions, vehicle’s locality, fuel consumption, load, and temperature monitoring. The information is also transferred via mobile connection to the local gateway and analyzed on the fleet operation platform. After it, the action ( for instance, an announcement on the vehicle’s display for a motorist about the overspeeding) follows.
Check our blog post about how to create a location-based app and particularities of its development.
With the help of IoT applications in the automotive field, fleet management has become more innovative and money/time-saving as there’s no need for manual work nowadays. With constant data monitoring, companies can deliver immediate advancements to the whole system. It also helps reduce the costs of fuel and maintenance.
3. In-vehicle infotainment
In-vehicle infotainment (IVI) means the integration of numerous internal and external systems for giving information and entertainment to both drivers and passengers. IVI functionality is controlled and manipulated via the touch screen panel of the head unit. It can be performed through a button panel, steering wheel, and voice commands too.
The main features of the modern IVI systems are:
- multimedia support. You can stream audio and video data from the smartphone, tablet, etc., through USB, Bluetooth, and HDMI cable;
- the big amount of maintenance functions and information are displayed on the head unit (Tesla took a step further — they included all the vehicle functions in the infotainment display);
- the pairing of smartphones via Bluetooth connectivity with the ability to perform almost all phone features;
- the integrated platforms — Android Auto and Apple CarPlay, which mirrorg your phone on the car’s display, and thus — reduce the level of distraction during driving.
Almost all the apps can be used in your vehicle (such as GPS navigation maps, music apps, social media, apps for audiobooks and podcasts, etc.). You can manage your incoming/outgoing calls and messages by voice commands which is very comfortable while driving.
Although nowadays a smartphone can be connected to a platform only through the USB cable, some brands have started to manufacture cars with the wireless connection, and this tendency will continue developing.
4. Predictive maintenance
Usually, the following two methods of car maintenance are used: preventive and predictive.
Preventive one means that when you know some problem is about to occur, you go and repair/replace what is needed. A predictive method actively leverages the IoT cars’ means to track all the parameters in a car on a real-time basis. If some problem emerges, the onboard system will inform the driver.
Nowadays, all the cars on the road have IoT solutions that usually consist of technologies for wireless connectivity, low-cost sensors, cloud computing, and Artificial Intelligence. With these solutions, an owner can determine any part breakdown before it occurs, which helps save money and increase safety. Sensors installed on car parts can even calculate the remaining service life of its parts and possible repairs needed in the future.
5. Advanced car insurance
There will be a huge impact on insurance premiums with the usage of vehicles and IoT concerning the individual driving style, the condition and mileage of the car, the locations where it drives, and other aspects. For these purposes, such IoT devices as an odometer or in-vehicle telematics are actively used, which are usually installed into specific ports in a car.
This IoT approach is beneficial for drivers too, as there is a formula “the safer you drive, the lower you have to pay for your insurance.” There are a lot of so-called UBI (Usage-Based Insurance) programs. Its main idea is “pay as you drive.”
The program is based on IoT data collection: you can voluntarily sign up for the UBI and freely sign out. An insurance company installs in your car a telematic device that is connected to a smartphone app. The device collects data and then sends it to insurance companies that set your premium based on your driving skills. Some companies, such as American Family Insurance, have already implemented the app, which doesn’t require any telematics devices and gathers data only through GPS and other location-tracking features.
Key points to consider when developing an automotive IoT app
There is a variety of IoT applications in the automotive industry, and the tech stack for each of them must be selected individually. Here we suggest you read about the general points which will be true for any IoT app.
Contact us, and our experts will find the best solution based on your project needs.
CONTACT USSoftware is a constituent component of the vehicle IoT system; however, one should be prepared to contribute a lot of effort to the selection and implementation of the other IoT components: tracking devices (RFID, GPS, satellite and cellular devices, geofencing), IoT protocols, server (cloud/cloud-agnostic), and user interface.
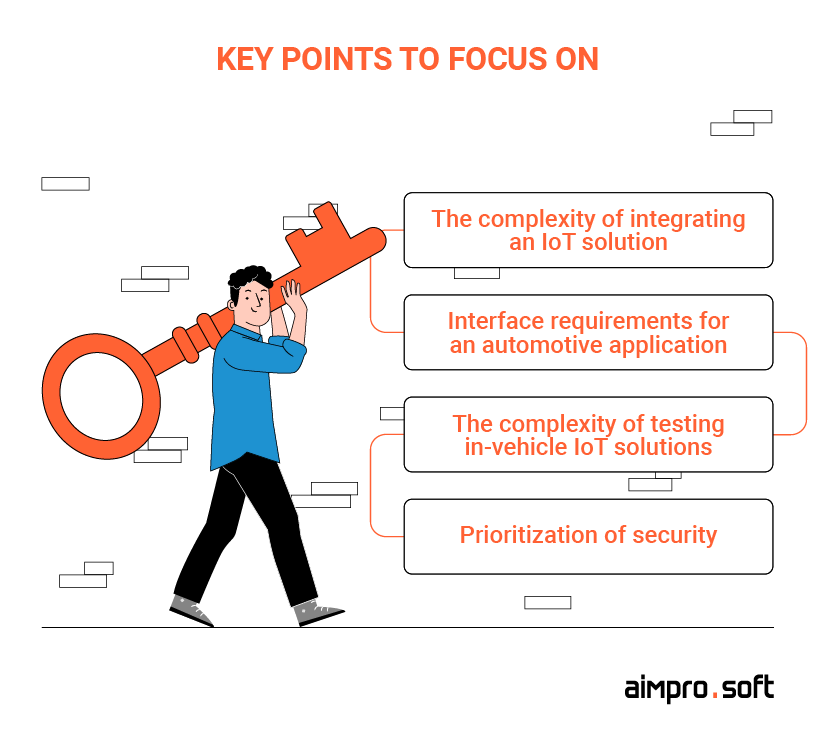
Key points you need to focus on
There are certain specifics of IoT apps for vehicles that will require your attention:
- The complexity of IoT solution integration into the whole vehicle system. The solution must be integrated with the onboard car computers by using certain hardware devices which require specific skills.
- The UX requirements for a car app. Automotive apps’ interface needs to be clear and simple, so a user won’t spend additional time puzzling everything out.
- The complication of the testing part for automotive solutions. To guarantee the full operational capability of the products, they must pass tests in different environments: in the laboratory, on the road, and in a virtual environment. At Aimprosoft, our QA team can help you successfully manage the following essential software testing: performance, interoperability, security, and access control, functional and usability testing.
We strongly advise you to start creating an IoT app for the vehicles from the MVP. The list of features required first and foremost are the following:
- access control;
- maintenance control;
- remote control;
- integration with proprietary equipment;
- security;
- voice control;
- automated driving (autopilot).
When developing automotive apps for smart vehicles in the context of the IoT, prioritizing security becomes imperative. Neglecting security measures in any component of the IoT system could expose vulnerabilities that cybercriminals may exploit, leading to potential harm. Various types of attacks, such as Man in the Middle (MitM), Denial of Service (DoS), service hijacking, and personal data theft, pose significant threats. It is essential to ensure that automotive apps adhere to the highest security standards, with security measures integrated right from the beginning of the development process.
While the technology stack for IoT app development can vary depending on the specific project, it is crucial to focus on the following key elements:
| Database | SQL: MySQL, Oracle Database, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server NoSQL: MongoDB, Apache Cassandra, AWS DynamoDB, Apache HBase, Google Cloud BigTable, AWS Timestream |
| Cloud server | Amazon Web Services, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, Cisco IoT Cloud Connect, Salesforce IoT Cloud, etc. |
| Backend | Languages: Node.js, Java, PHP, Python, .NET, Ruby, JavaScript |
| Frontend | Languages for iOS: Swift Languages for Android: Java, Kotlin |
| Geolocation | iOS: CoreLocation framework, MapKit, Google Maps Android: Google’s Location APIs, Google Maps Android API, Google Maps |
| Payment integration | PayPal, Braintree, and Stripe |
| Push notifications and SMS | iOS: Apple Push Notification Service Android: Google Cloud Messaging, SMS notifications — Twilio |
Creating a robust IoT-based software is full of nuances and challenges. If you want to know about it in all details, check our blog post
Finally, we want to draw your attention to another two characteristics worth mentioning — the maintenance of the server-side components, which will let you update the whole app by adding new features, and the app’s scalability, which is certainly needed in terms of the stable work despite the amount of workload.
Our experience in using the Internet of Things for the smart vehicles
A client who produces chargers for electric cars came to us with the idea to let their clients — car owners, remotely control the charges with the help of an IoT solution. The interconnection of three elements formed the basis of the product. It was designed to consist of the charger, the board (a controller inserted in the charger, which connected to the server and sent commands), and the native mobile apps for iOS and Android that we were ordered to develop.
To implement the best options for software architecture, our iOS engineers chose MVP (Model-View-Presenter) and the Android specialist — MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) architectural patterns. The client opted for two user roles with different responsibilities in the app. Therefore, we designed logic for the owner role and for the user.
To configure the app settings, the owner needed to scan the QR code (which was a unique identifier) on the charger and connect the controller to the Internet. The owners’ available features were to monitor the charger via the app (whether it is plugged in or not, charges a car or not), to share the rights to charge a car for other users and remove the user if needed.
During development, our IoT engineers faced the challenge of removing the logging process on the controller’s SDK to make the interaction with the app easier for users. To get in advance the charger’s ID without logging procedures, our specialists improved and adjusted the SDK code by changing the limitations of the existing solution to the client’s needs.
As a result, the users could control their charger remotely with the ability to turn it on/off, configure the power of the charger, and switch between available chargers (if there are a few of them). The app appeared to be one of the good IoT use cases in the automotive industry that contributed to the electric car charger sales: now it has 10,000+ downloads on the App Store and Google Play Store.
Don’t hesitate to contact us; we will examine your request carefully and suggest the best-fit solution.
CONTACT USConclusion
IoT in the automotive industry has made a big impact on the whole car concept, which is actively being reconsidered these days. People expect their cars to be a whole software platform with easier control and interaction and with functions like self-driving. IoT technologies can be used by manufacturers to enhance both the production process and the development of better car systems. One of the hottest topics is car maintenance which contributes to the economy, car safety as well as in-vehicle infotainment because driving today is turning drivers from the stressful control of the road to an exciting journey.
If you bear the idea of creating a car IoT app and want to be on the frontline of the automotive field digital transformation, contact our IoT development team to take a step forward to its fast and efficient implementation.
FAQ
What difficulties may I face when developing an IoT automotive app?
When developing IoT applications in the automotive industry, you can face the challenge of integrating them into the whole vehicle system. For this, it must be integrated with onboard car computers using certain hardware devices requiring specific skills.
The next difficulty is testing an app. All apps integrated into a car IoT must be strictly tested to prove their full operational capability. For this purpose, the testing must be held in different environments like a laboratory, road, and virtual one. The following software tests are essential: performance, interoperability, security and access control, functional and usability testing.
The big question of concern for developers is security. Considering that all the data collected through IoT means can be reached remotely with access to just one of the IoT devices, it is crucial to think about a good security system at the initial stages of app development.
What are the payment solutions in connected cars?
This function is actively embedded in IoT connected vehicles’ IVI systems to make payments as simple as possible for the driver, which is especially meaningful when you make payments for such commodities as parking lots and toll roads on a routine basis without any distraction. This provides the convenience of payment without distracting the driver. For manufacturers and businesses, it opens up opportunities for new partnerships and collaborations with retailers, enabling contactless pre-orders and payments.
Implementing payment solutions in can include RFID, BLE hardware, or third-party APIs, with a focus on supporting different gateways and robust security features. However, integrating mobile app functionality into a vehicle’s head unit is challenging, which some companies, such as Visa and SiriusXM, are addressing by developing e-wallets integrated directly into the dashboard with voice control capabilities.
Which safety specifics do Iot car have?
Smart cars and the Internet of Things actively leverage road safety for drivers and pedestrians. Integrated IoT technologies help the driver monitor surrounding conditions, react to changes, or take full control of the car in emergencies. Now, most cars have safety features as built-in options (like Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems), but the extra services such as automatic speed limiting or blocking texts can be implemented by plugging into the onboard diagnostics (OBD) port.
What is the future of IoT in cars?
The future of IoT in cars is incredibly promising, focusing on increasing connectivity, automation, and data-driven information. This will enable advanced safety features such as collision avoidance systems and intelligent traffic management. Personalized experiences will become the norm as connected cars integrate easily with other IoT devices. In addition, IoT will revolutionize maintenance practices by enabling predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and optimizing performance.
How is the automotive industry using IoT?
The automotive industry uses IoT in a variety of ways. It uses IoT to track and monitor vehicles, enabling efficient fleet management and logistics. IoT provides predictive maintenance, allowing manufacturers to identify potential problems before they escalate. In addition, IoT enables advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), improving safety on the road.
Is a smart car an IoT device?
Although smart cars can use IoT technologies, they are not usually classified as separate IoT devices. Smart cars can more accurately be classified as cyber-physical systems that implement IoT principles. However, the term ‘IoT device’ usually refers to separate, independent devices that connect to the Internet and exchange data. Therefore, while smart cars use IoT concepts, they are not considered traditional IoT devices in the same sense as autonomous sensors or appliances.
What are the applications of IoT connected car?
IoT cars offer a wide range of applications and benefits. For example, connected cars IoT also supports intelligent parking solutions, allowing drivers to find free parking spaces quickly. In addition, in-car infotainment systems provide personalized content and services, creating a more enjoyable driving experience.
What is the impact of IoT on vehicles?
IoT transforms vehicles with enhanced safety through proactive maintenance, early fault detection, and real-time monitoring. It optimizes fuel consumption by leveraging data-driven insights and improving engine performance. IoT enables seamless connectivity, integrating vehicles with smart city infrastructure for better traffic management. Enhanced driver assistance systems, like lane departure warnings and adaptive cruise control, further enhance safety and comfort on the road.




