How to Create a Location-Based App: Strategy and Process Roadmap
Key takeaways
-
Learn more about how to make a location-based app using outdoor and indoor positioning for different industries applications.
-
We highlighted consumer interest and business opportunities in the location-based services market implemented in the well-known cases.
-
Know more about top ideas on how location may be applied in human life.
-
Tech stack behind the GPS mobile app development and cost of launching your project.
-
Study Aimprosoft’s expertise in two cases for telecom and delivery sectors.
With the popularization of geolocation technology, our phones have become the doors to a more friendly and convenient world. Almost everyone enjoys its advantages: users leave the geolocation function turned, utilize a photo location finder option for outdoor geolocation purposes, and investigate the areas deeper.
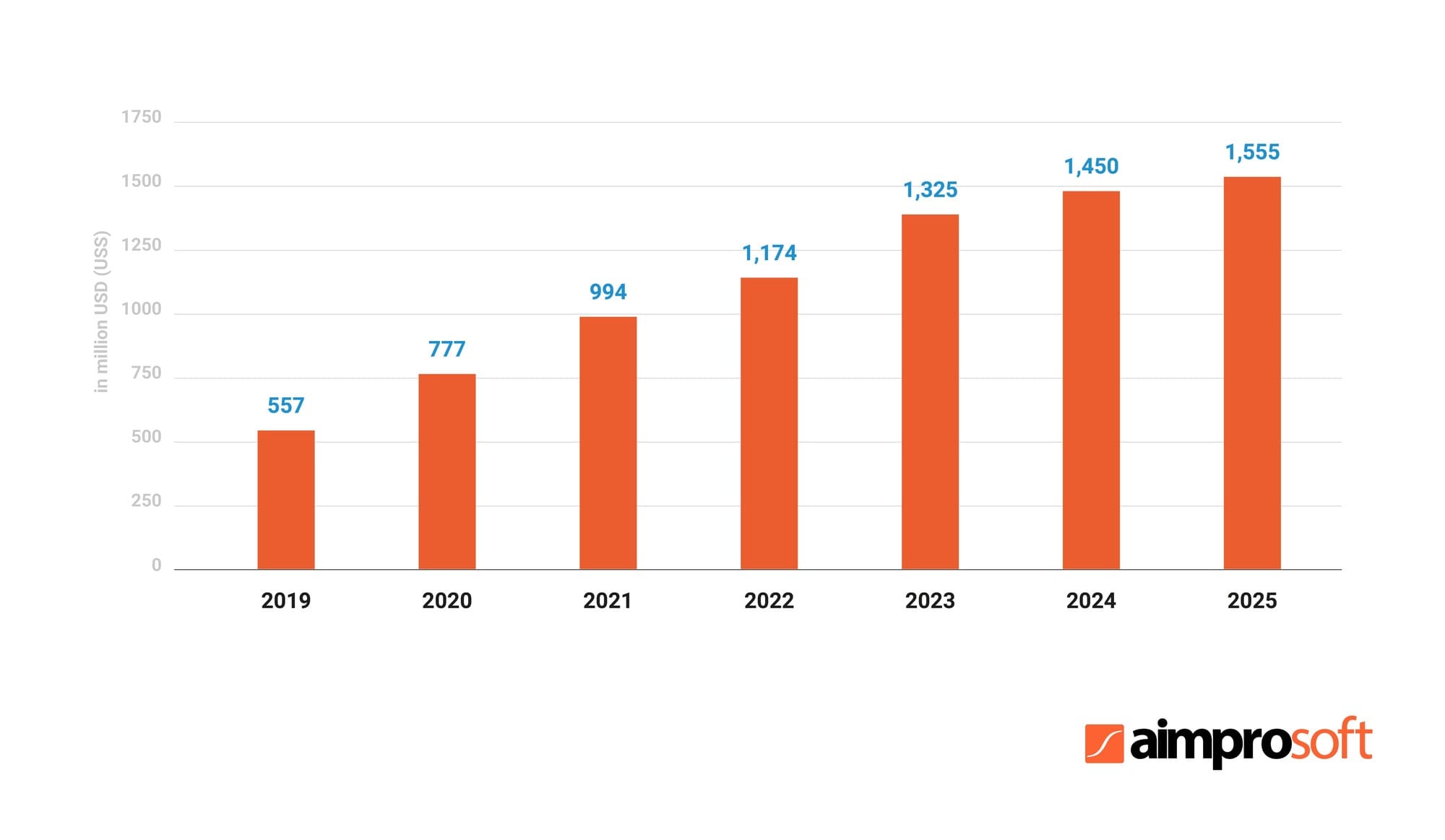
2021 is almost off and we will know soon if the forecasts in the navigation segment will reach the projected $994 million. Considering this statement, a business can massively benefit from geolocation in all its diversity including the most specific consumer needs. Based on smartphone usage statistics in the US, the developed app will be able to expand your audience by more than 240 million customers.
So how to create a location-based app? Let’s hit the road to find it out!
What is a location-based mobile app and why is it useful?
Location-based applications concentrate services around the user location, which is determined by a global positioning system (GPS), Cell ID, Beacon, or similar technologies.
Most of these technologies serve as a navigation tool for route tracking that allows a user to find the right places, the road to these places, or a particular person. But there are also geosocial, gaming, commercial apps, as well as many other types that make the most of geolocation functionality. Let’s rationalize what is so attractive in GPS-based apps for users and how you can win their hearts if you make a GPS-based app?
USERS INTEREST IN GEOLOCATION APPS
Navigation
Find a place, explore how to get there, look which of your friends are there, look at prices, special suggestions, and feedback — all this on one screen immediately improves user experience and saves the customer time.
Commercial
The consumer receives valuable and timely information about current promotions, discounts, recommendations and gets personalized ads and purchase offers, which allows avoiding places with poor services. In addition, users are often involved in evaluation and recommendations, which gives them a feeling of expertise. At the same time, a business gets free content for customer engagement and retention on the principle of social media networks with geolocation services. Isn’t it a great chance to please customers when you create an app that uses GPS?
Entertainment
Locational features are used in games to expand gameplay using the world around them. Together with the AR, it gives a unique experience. The resounding success of Pokémon GO is a great example of extraordinary GPS mobile app development.
Social
The fact that users love to demonstrate their lives to other people is proved by personal daily pictures on Instagram and detailed profiles on social networks. Since social networking was characterized by static information, the geolocation applications made it possible to add dynamism to this process by providing the user’s location. Do you want your friends to know that you are at a show of your favorite band or at the World Cup final? One finger movement and all the friends will be able to see it.
You may be interested in building a social network article. We can get you covered there.
Security
In addition to not getting lost in an unfamiliar place with the phone at hand, the location function allows tracking the user’s movements to family members or friends if they are worried about him/her. Some apps automatically send text messages to the close ones when the user has reached a destination: work, school, or just came back home at night. It is reasonable to make a GPS app for better parent control over kinds.
Wheather
Among other GPS applications, the weather forecast is worth user attention. People long to all go as planned. As the weather is the most variable thing, weather apps are considered as the hope to bring a bit of stability into human lives. Hundreds of weather apps in the app store are of high-demand services, among which Weather Channel, Yahoo Weather, AccuWeather, and AccuWeather are operating by using location data.
BUSINESS INTEREST IN MOBILE GPS LOCATION APP DEVELOPMENT
Attracting more customers
By using geolocation apps, you get access to consumers at their most unprotected point in time, inducing them to make unintended purchases. Getting into the area of your establishment, the buyer will receive push notifications about discounts, promotions, and other offers near themselves. Such new ways to replenish the audience are the shortest way to increase profits by the advantage of location.
Personalized experience
Location-based apps allow you to collect useful information about customers based on their registration in certain areas, reviews, and purchase history. It gives the business an advantage to customize individual offers with location-aware content and develop a global marketing strategy.
Brand awareness
Geolocation technology helps increase visibility, as it becomes, in fact, a separate and powerful source of advertising. Consumers will find your store easier because as they walk past it, they will receive a push notification about your best offers and discounts. The marker of the store on the map with all the necessary information and users’ reviews will contribute to the store traffic. That’s one more reason for startups interested in how and why to build a GPS app taking into account business interests.
Virtual tours
Hotels, hospitals, and any other institutions can be explored in more detail due to the virtual tour feature. With the help of AR technology, the users will be able to find out everything they need, looking around through the phone’s camera: from how to get to the right department, to where to find the right product. This is also useful for stores, as it will reduce the number of consultants or remove some workload from them. Virtual tours will simplify navigation and optimize the work process of your institution.
The most popular industries using geolocation
The list of m-commerce app functionality is clearly regulated. First of all, these are the functions that are focused on the sale and everything related to it: search, addition, purchase, and much more.
According to Kantar TNS statistics, the most popular use of location-based apps is navigation (46% of respondents), search for restaurants (26%), and finding friends nearby (22%) closing the top three. However, there is a much broader range of industries where it is reasonable to create a GPS app with highly beneficial adaptation.
Retail
The full commercial potential of geo-technologies is revealed in retail: GPS technologies help customers find stores nearby or select an acceptable delivery point. Customers will choose the most convenient store with a mobile shopping option, so the competition for an audience is won by the most convenient retail location-based solution. Among the most famous representatives are Ikea, Walmart, and Target.
Dating
The social value of geolocation apps is often higher than the navigation component. It’s fully used by dating apps like Tinder, Happn, and OkCupid. In them, the search parameters of the mate are adjusted to the geolocation, and it works on the same principle as in the retail industry. Just like a customer can make an unintentional decision to visit a store if he/she sees location-based notifications about a favorable discount nearby, the user of dating apps can wish to meet with a person because he/she is near on the map. Today, the annual turnover of dating apps is over $139 million, and their creators demonstrate an incredibly inventive approach to monetization. Dating apps make money with ads, subscriptions, premium purchases, gifts, and other paid functions.
Games
Some choose to make a geolocation app to earn by entertaining. The gaming industry today is one of the most profitable, regardless of the platform. Geolocation can be used only by portable devices, the most common of them being smartphones. In games such as Pokémon Go or Walking Dead: Our World, the usual gameplay is enriched with AR elements, allowing you to get a new experience from the game. The vast majority of such projects are distributed free of charge, but they are called free-to-play for a reason: a user may spend even more cash than with a one-time purchase.

Travel
Any booking or travel app has a map so that the user can determine which public places and attractions are located around, as well as how to get to the necessary points. For tourists, a reliable source of navigation is a real magic wand. Usually, such apps earn through advertising, booking fees, and partners’ investments. This allows companies like Airbnb, Booking, and Tripadvisor to earn millions every month, as this industry is characterized by an excellent economy and tons of monetized traffic. Apart from navigation through smartphones, a GPS module is a navigation device that features low power consumption and high sensitivity being highly appreciated for sneaking through virgin forests and hiking mountains. It also rely on the same technology.
The world is recovering from COVID-19. It’s time to travel again. More about the online travel portal development here.
Fitness
People who are involved in sports love order and consistency, without which it’s impossible to achieve high results. Fitness apps with geolocation are aimed primarily at sports fans that overpass the distances and destinations like runners and cyclists. Such applications help to pave the best routes, mark the speed, seek other athletes nearby. Users can share their statistics, publish favorite courses, and compete with other runners online. Startups can make money through subscription, advertising, and paid options, like in running applications Runtastic and Runmeter. Large companies can expand their brand like Nike with its app Nike+, Nike running club, and fitness trackers.
Automotive
In addition to the option of tracking down the traffic jams, startups can make money by providing a search for the nearest/cheapest gas stations, restaurants, as well as monitoring vehicle movement like in Moovit. Enterprises can manage fleet or transportation systems with location-based apps like Geotab and Bringg that allowing them to track and control logistic issues. Among the main advantages of automotive apps in terms of earnings is that their average price is higher than the price of other apps, which allows them to monetize it in a better way. Otherwise, they make money the same way as others: a paid subscription with paid options and advertising.
Top cases of successful location-based apps
Most of these cases were successful because they were the first who have implemented a new idea on the market. Being able to understand the needs of time and give it to people is the most effective path to success.
Transportation — Uber
The creators of Uber were the first who saw untapped potential in geolocation feature usefulness for ordinary pedestrians and embraced the idea to build a location-based app that became no less important for passersby, than for drivers. Uber made finding and hiring a taxi as comfortable as ever: bilateral location technology allowed customers to monitor a taxi on the map, and drivers could track the exact location of the client. The ability to put stars motivates drivers and correlates with a trend of mass rating.
Uber earns through taxi services; location-based technologies serve as support of the concept leveraging real-time information. According to CNBC, the Uber valuation as at Q1 2019 was $3.10 billion. Witnessing such success, it’s quite clear why many want to be like Uber.
Dating — Tinder
The Tinder dating app was launched in 2012 and differed from the competitors by the search of partners in a habitat zone. GPS functions increased the likelihood of real acquaintances of users, tracking feature shows to potential matches your favorite places, and the image-oriented design with the lack of redundant mechanics such as registration and surveys made it possible to stand out among the competitors.
Tinder’s outstanding financial success — in Q1 2019 the company earned $260.7 million, — explained by experts that company was among the pioneers of the access economy and successfully adapted people’s desires to find a soul mate for the realities of accelerated modern life.
Social — Foursquare
Foursquare social network is the first concentrated all its services around the benefits of geolocation. The app allows marking places you visit and get points for check-in public places, which can then be spent on various bonuses. Foursquare is available for both smartphones and mobile phones without GPS, which will still successfully interact with it due to LBS technology.
After the separation in 2014 into two services, Swarm and Foursquare, the latter leaned toward business needs. The company earns 90% of its revenue in partnership with corporate business, which is attracted by the software solution and the array of user movements data. Even after 10 years, Foursquare has no analogs and remains a unique offer for a business.
Gaming — Pokémon Go
Before Pokémon Go, mobile games with geolocation and augmented reality were already coming out but never had such a success. Social interaction and revolutionary gameplay became a reality with GPS integration.
A separate feature of the monetization was Lure modules, which attracted Pokémon to a certain territory. The cafe and snack bar owners successfully used it: Linizio, a New York-based pizzeria, raised its income by 75% after the manager spent $10 on Lure modules in his establishment. Such a system shows itself to be hugely successful: over the past year alone, Pokémon Go made almost $800 million.
Shopping — Curbside
In contrast to the times of traditional e-commerce, modern customers are not connected to the desktop but move throughout the day with mobile devices. Location-based shopping service Curbside allows the user to track an order through GPS-signal on the mobile app and pick it up on the same day at a convenient time and place.
The user publishes an order online, suitable for specified location parameters retailer or restaurant fill it, and then the user receives a notification that the order is ready. The app informs the store employees about customers arriving, after which they immerse the products in their car.
Curbside cooperates with most leading retailers and restaurants like Target, Best Buy, Boston Market, which allows customers to have a wide choice for fast and comfortable shopping near the home or work. Also, the company distributes its SDK on a paid basis for those who want to use it in their own applications.
Looking at how many industries are already successfully using the fruits of geolocation, it may seem that there is no longer a new use for it. But this is deceptive: the potential and prospects of location-based apps are greater than ever, and ideas for the implementation of GPS-related functions are held back only by imagination.
Top ideas to make a GPS-based app
Recommendation apps
Most location-based apps use the principle of connection places to people. But what if you go in the opposite direction and let people share their favorite places for a certain type of activity? Such apps could succeed in the fitness industry (the best routes), dating (the best places for dating), even surfing (the best big wave beaches). Technically, this works with the simplest mechanism of putting marks on the map, which is easy to implement. At the same time, it is very likely to succeed among its audience, taking into account there are still no competitors on the market.
Augmented reality
Augmented reality is already being used in mobile games, but this technology has the potential to enrich many location-based apps from other industries. For example, the most popular augmented reality use cases are navigation and tourism. Just imagine that you can ‘scan’ the surrounding area with a camera for any information: from historical facts about the city attractions to recommendations and guides for the nearest and best stores or places. UB Travel is one of travel apps that allows you to create your photo maps or view others.
In the retail business, AR can be used as a part of quality service for working with clients. It helps with a search for a specific product: in large stores, it is difficult to find something specific, but AR applications can locate the user and graphically show the path to the desired thing, updating the rest of the products in real-time, with their price, reviews, and discounts. A good example would be Lowe’s Home Improvement app, which helps you navigate through a huge hypermarket when searching for the right products.
For real estate, AR can be an innovative solution when acquainting buyers with the object. Clients will be able to save a lot of time when selecting houses and apartments, and unfinished houses can be viewed in full detail in a digital 3D view, which will significantly increase the likelihood of making deals. For example, Realtor.com application allows you to search for houses and apartments by signs directly from the camera, as well as to get acquainted with the details of any found home for sale.
The introduction of AR game elements can be applied in the most unexpected apps. Users of fitness applications may diversify their run by escaping from the hordes of zombies in Zombies, Run!. Educational apps will become clearer and more interesting with visualized elements: in astronomical app Vortex Planetarium the night sky is much easier to learn with graphical tips. You can earn on such products by pay-per-download distribution. If you want to learn more, read our article about creating educational apps.

Location-based AR apps work on comparing GPS data from the mobile and digital compass to determine the location details of the device. When receiving location data, the application can define where to add visual elements to the real world.
IoT apps
The prospects for the growth of IoT location-based apps are almost limitless because most of the gadgets and solutions already have access to GPS. This allows you to find a lot of synergy between the app and the surrounding objects.
Custom geolocation solutions will help make your smart home an almost living organism where the intellectual environment responds in different ways to the user arrival and interaction. So, applications that are integrated with home devices will turn on the light and launch specific tools like a thermostat when an owner enters a home. The user also receives alerts when someone else enters or leaves the house. With the help of geolocation technologies it is elementary to program, let’s say, a refrigerator to report what products are missing when you walk past grocery stores.
Geolocation opportunities in the field of IoT are not constrained by four walls. They can help in the intellectually built environment of the city. You can track traffic, parking spaces, movement of goods, and so on using wireless sensors. The IoT sector and location-based apps hide massive potential for business because people are ready to spend money on making life more comfortable. We can see it on the example of such smart home apps like Apple Home and IFTTT spreading in recent years.

The location-based app sector is popular despite its young age. The example of Foursquare, Uber, and others allows us to see the companies that were the pioneers in this business 10 years ago. Now they are the world leaders of their industries. Investors should pay attention to the geolocation app development for several reasons: first, this area continues to actively develop and form new approaches in implementation, which means excellent ground for startups. Secondly, the statistics for the last 10 years shows the very rapid growth of businesses owning geolocation apps, from startups to enterprises.
How to develop a location-based app
Now let’s move to the hot question: how to build an app that uses GPS and to translate your abstract ideas into binary code? For successful app development, you need to know the list of technologies and tools used when creating geolocation products.
TECHNOLOGIES
All this tech stack, except for indoor geolocation ones, is built into modern devices by default. Consider them as providers: if one of them loses connection, another one activates. Outdoor navigation like Google Maps
GPS
The most common location technology to date, GPS, locates the object due to satellite signals. Positioning is done through geometric trilateration: based on reachable satellites, the smartphone identifies the GPS coordinates of the owner. It requires at least three satellites at the same time for regular functioning. With advantages such as high speed and accuracy, tangible drawbacks coexist, such as high battery power consumption and dependence on the terrain conditions, which may influence user experience. Nevertheless, the GPS benefits of availability and effectiveness far outweigh its shortcomings.
Cell ID
If a GPS signal is not available for some reason, you can use Cell ID as a location technology to get cell tower data. The smartphone will know where the owner is located by following cell phone towers that serve as a coordinates guideline. It relies on radio signals of the operator and needs suitable environmental conditions. The advantages of the Cell ID are that the geolocation function will be available even without a GPS signal, but in return, this approach can’t boast the same positioning accuracy, which deviations can reach several hundred meters.
Assisted GPS
A-GPS technology is a symbiosis of GPS and Cell ID: the location tracking process is accelerated due to the synergy of cell towers and Wi-Fi geolocation. As a result, GPS positioning gets greater accuracy and speed. The Achilles heels of geolocation technologies like tunnels and forests in the case of A-GPS do not affect the successful operation. Instead, many A-GPS devices are very dependent on the outside server and can not be run standalone, which combined with the constant need for a Wi-Fi connection, complicates the smooth work of this technology. Using A-GPS implies some problems with private data protection since contact with a third-party server allows seeing your position. Nevertheless software vendors ensure the data safety on the appropriate level.
Wi-Fi
In the location-based mobile app development, Wi-Fi is used in two ways: via RSSI or Google Maps. The RSSI method (Receive a Signal Strength Indication) is implemented by comparing the cellular data with Wi-Fi points. When selecting GoogleMaps, the profile of frequently visited locations within Wi-Fi access identifies the location of the client, after which the user is marked on the map. The ease of use and the identification speed contradict the dependence on the coverage area, which is much lower for Wi-Fi compared to GPS.
Beacons
A completely different approach when you build a geolocation app is demonstrated by Beacons Indoor technology. It is implemented using beacons, small wireless transmitters, and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy), which beacons use to send as a signal to the user and determine its location.
Depending on the platform, Beacon’s technology will be different: iOS supports iBeacon API out of the box. Eddystone, another format by Google, can be used both on Android and iOS devices, but if you want to operate it on Android, you need to write your own implementation or use the AltBeacon library. iBeacon and Eddystone have a high detection accuracy and the ability to work without the Internet. Among the shortcomings are the significant initial investment and support for the viability of the transmitters in the future, as well as a small coverage radius. You should pay special attention to this option if you need to set up indoor geolocation.
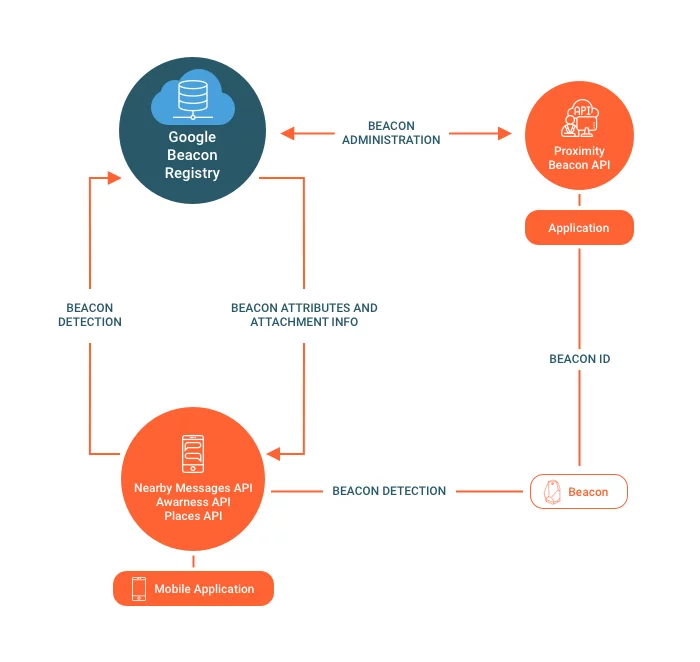
Geofencing
The youngest among the presented location technologies, Geofencing utilizes a virtual field around a physical object, that is created to establish the user’s location. Detailed information about the location is identified in relation to a certain point: how geographically close they are, inside or outside, what time they entered/exited, etc. Geofencing coverage range is up to 500 meters, and the range of business applying is even wider: from sending offers to providing a personalized experience to the customer.
A lot of business opportunities and a larger radius of coverage than BLE coexist in Geofencing with high cost and energy consumption, as well as the slow client’s adoption rate. In business, it is used to improve marketing and connection with clients.
API AND SDK
To develop location-based apps and use the above pool of technologies, you require to integrate APIs and SDK. It is a set of structures and libraries through which an app can interact with other features instantly. In case of location-based apps, APIs vary by platform and allow to use them as ready-mades because the developers of software kits have already implemented these location functions.
All you need is to connect one or two APIs. The main API determines the location of the user, and the secondary is responsible for the visual design of geographic objects, various marks, and maps in general. It is possible to use only the main API in cases where your app performs location functions without the need for visual display on the map.
The list of iOS APIs for positioning:
- Google Maps Geolocation API. This is one of the most popular map services around the globe. It covers 99% of the earth’s surface and is characterized by ease of integration, flexible customization (including the color of the map, the density of roads, the level of detail on the map), and support for many languages. Google allows using it for map-based app development without paying for free applications, but for an enterprise, you will need to purchase a license.
- Apple Maps. It enables to add annotations, view 3D maps, and gives complete control over the map management (zoom, rotate, pan). Besides, Apple Maps provide user positioning and step-by-step routing with voice guidance, using the direction API. The advantageous difference between Apple Maps and Google Maps API is that it is free: Apple Maps’ beta testing is not completed, and it requires an Apple developer account to install.
- Core Location API. Developed by Apple, this technology is focused on determining location, height, orientation, and position relative to iBeacons. CLLocationManager methods and all built-in capabilities are used for positioning, including GPS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, magnetometer, accelerometer, and cellular communication.
- Google Places API. A free web service API, Google Places are used by app developers to query geographic locations or any points of interest nearby to any given point istead of build up a database with local bars, shops, restaurants, cinemas, etc.
The list of iOS kits for displaying:
- Apple MapKit. MapKit framework displays maps and allows you to interact with them in every possible way: show the current location, add reviews and overlays, specify routes, etc. Like Apple Maps, it is free to use.
- Google Maps SDK. With this SDK, you will be able to build a location-based app with automatic access to Google Maps servers and maps display. There is one pricing plan for using: Google gives free $200 for use every month, and those who do not exceed this amount will be able to use it for free. When exceeding the limit, you must pay only for the services you use. Price table of the Google Maps SDK can be found here.
The list of Android API for positioning:
- Google Location Services API. In place of outdated in all respects Android.Location package, Google recommends using this API. Google Location Services (GLS) is easy to use; it achieves greater accuracy, and the battery drains less compared to the outdated kit. Using Google APIs, you can determine the location through all the technologies available to the device, identify the movement of the user, and define the distance to a particular place.
The list of Android APIs for displaying:
- Google Maps and MapView class. The combination of these elements ensures easy visualization of the maps. Bear in mind that Google Maps only works on devices with Google Play Services installed.
- Google Maps Directions API. It performs the function of routing and guides in specified directions. Supports walking, cycling, as well as public and car modes of transport.
- Google Distance Matrix API. Calculates the approximate time of the route, depending on the density of traffic, transport, and other variables, for example, to allow users by 1 request get the nearest store or ATM.
Besides, there are many third-party, neutral towards platforms APIs. They can be used as an addition to the officially recommended APIs for the integration of extra features. The most common purpose of their purchase is to use databases with information about places, reviews, ratings, and recommendations of users from such large companies as Foursquare, Facebook, Tripadvisor, Urban Airship, and others. They differ by the size of the database and individual capabilities.
Process for MVP
Now we have come to the question of how to create a native application that uses GPS location information. Let’s start with an MVP of the app that allows you to track GPS-based positioning and save your user’s location history. For a demonstration of the product viability, the implementation of the key features is sufficient:
- Authentication;
- Settings options;
- Push notification;
- UI/UX.
For spot determination, you will require geolocation features that are distinguished from the usual app:
- GPS tracking;
- Map visualization;
- Check-in;
- Location history.
To create a location-based app MVP with these features, you will need:
- 1 Project Manager;
- 1 UI/UX designer;
- 1 Tech Lead;
- 2 Backend developers;
- 1 iOS developer;
- 1 Android developer;
- 1 QA engineer.
Such MVP can display a user’s location on the map, send information to the server, and notify you of approaching certain objects.
How much does it cost?
The cost of an application is determined by the number of integrated features and hours spent. Each project is unique and has its price and time frames, but we have prepared an estimate that will help anyone understand the price to make an Android app that uses GPS or its iOS alternative on a turnkey basis.
Creating a full project will require an increase in the development team and additional features that are designed for more comprehensive use of geolocation, such as:
- Places integration;
- Rating and recommendation;
- Bilateral location sharing with friends.
The business analysis may take 25 hours and over if you have a clear picture of the project’s specifics. Together with 15+ hours of technical specification, it is a theoretical foundation of the work, without which successful location-based application development is impossible. Business analysis helps scrupulously gather your requirements and translate your idea into a software solution. On its basis, a rough and detailed estimation is prepared to provide you with a full understanding of the time and cost needed for the project.
UI (45-50 hours for MVP and 80-90 for a full project) is essential for building location-based apps because most of such products information is visual, so the simplicity and convenience of the design will directly affect the convenience of user orientation. Android GPS app development and iOS location-based software development will take from 80 to 120 hours for MVP with the most basic features, and from 120 hours for a full project with a broad functional palette. The QA department may take quite much time to test the error-free operation of the app — from 90 hours for each platform.
| Stages | MVP hours ~570—710 | Full feature hours ~830—1,000 |
|---|---|---|
| Business analysis + UX | 25—30 | 30—40 |
| Technical Specification | 15—20 | 20—30 |
| UI/UX | 45—50 for each platform | 80—90 for each platform |
| iOS/Android development | 80—120 for each platform | 120—160 for each platform |
| Backend | 100—120 | 160—190 |
| QA | 90—100 for each platform | 110—120 for each platform |
Special attention should be paid to the backend that includes a database (NoSQL ones: MongoDB or CouchDB), admin panel (HTML with CSS), and Node.JS for push-notifications support.
On average, the total project cost will be as follows:
| Country | Average hourly rate | MVP ~570—710 hours | Full feature set ~830—1,000 hours |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | $80 | $45,600—56,800 | $66,400—80,000 |
| Western Europe (Germany) | $65 | $37,050—46,150 | $53,950—65,000 |
| UK | $70 | $39,900—49,700 | $58,100—70,000 |
| Eastern Europe (Ukraine) | $40 | $22,800—28,400 | $33,200—40,000 |
Location-based app development with Aimprosoft
We at Aimprosoft successfully completed different projects with location technologies under our belt. Be it the classic GPS positioning or indoor navigation, our team knows how best to embody your most ambitious wishes in the app.
TIMECHECKERS DRIVE
The delivery industry is constantly looking for practical solutions for such pressing issues as effective management of employees and offering the highest level of on-time delivery services. To deal with these problems, Timecheckers Technologies turned to us. The Aimprosoft team set itself an ambitious task to solve two problems with one solution.
Our developers were engaged in the full frontend, backend, and Android location-based mobile app development, which has received the name Timechekers Drive. Such integrated location-based features as GPS and schedule tracking, location detection, groups of users allowed a client to track the location of employees at any time and distribute them into clusters depending on working shifts and transported goods. The flexible settings of parameters (interval, distance) and 4 tracking modes made it possible to track the movement of employees depending on customer needs, which was the solution to the first problem of the management of workers.
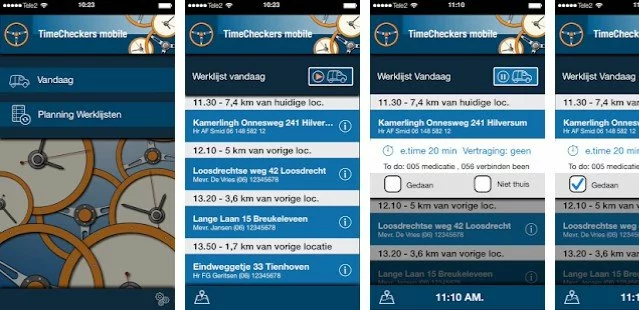
The number verification process is simple: the user sends an SMS to a short number, then receives a one-time password and enters it on the application. Besides, integration with a local mobile operator was made to send SMS notifications with the expected delivery time, support for a full two-way communication channel between the client and the driver, and rate the quality of the driver’s service not only within the app but also via SMS. With this decision, we dealt with the second problem of improving the quality of the on-demand delivery service.
As a result, Timecheckers Drive has become an incredibly convenient application for logistics, supermarkets and other retail organizations. This project was an example of a reward for courage in taking on an ambitious task and a talented incarnation in spite of everything.
MOBILE APP FOR TELECOM PROVIDER
Another project we are proud of was associated with indoor technology. A large German telecom company contacted us to create a mobile news app designed for spreading location-based content for users.
We chose iBeacon as the basis for solving the task. To enable the user to receive content according to the place where he/she is located, the developers used UUID (universally unique identifier) and ID of each article: getting into the beacon’s range, the application scanned the device’s UUID, selected the suitable for ID article and showed it to the user. Multimedia content came with pop-up push notifications and could be structured by the user into categories, archived and restricted in access.
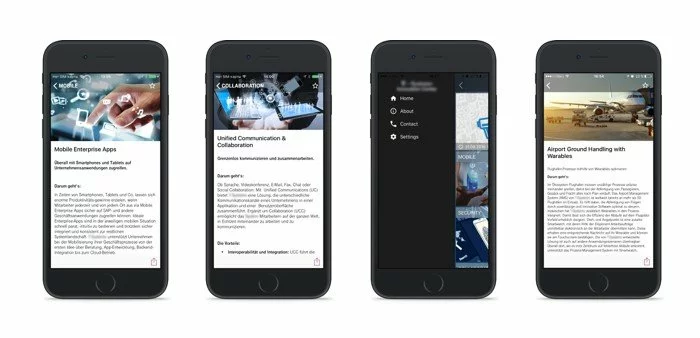
The iOS development process did not reveal the slightest difficulty, which is not surprising because Beacon technology is native to this OS. But for successful interaction with Android, it was required to use the altBeacon library and test it thoroughly. Besides, at the time of development, the beacons were not widely distributed, and our team managed to solve this challenge by using a smartphone as a transmitter of Bluetooth signal.
The news location-based application was developed for iOS, Android, smartwatch, and successfully operates to this day on all the platforms.
Conclusion
Just as a location-based app leads a user through unfamiliar places, so we led you to understand the significance of these applications for business. This is an area that is characterized by high growth, relatively easy development, rapid launch, and great prospects. We at Aimprosoft have repeatedly subordinated real space to digital measurement, each time successfully meeting high expectations of customers. If you have an idea for location-based mobile app development, do not hesitate to contact us and see how your dreams become a reality.
FAQ
How can you save money on geolocation app development?
You can create a non-native MVP using React Native so that you will have a working MVP for both iOS and Android. It will halve the cost of MVP creation. However, a fully-fledged product built on such an MVP will experience a certain loss of performance with limited access to device hardware and a lower security level.
How to win your geolocation app’s users’ trust and make them loyal?
Enable your target audience to choose between constantly tracking location, tracking only during its use, or permanently disconnecting it. Thus, they will have a choice in their hands when installing your GPS tracking app.
How to increase your application’s usability?
We can recommend the introduction of offline mode and caching so that the system can cache geo-points in the immediate vicinity and then reduce the load on the servers. This way, the system will not depend on a permanent internet connection.




